When it comes to structural engineering and construction, the choice between H-beams and I-beams is often crucial. Both types of beams serve essential functions in providing support and stability to structures, but they possess distinct characteristics that influence their strength and application. Understanding these differences can help engineers, architects, and builders make informed decisions for their projects.
Understanding H-Beams and I-Beams
Before diving into the strength comparison, it’s important to define what H-beams and I-beams are.
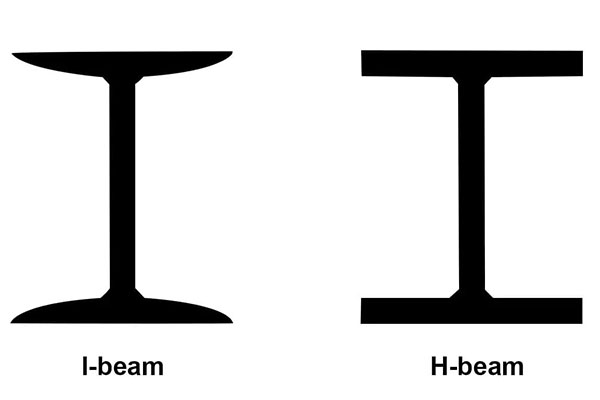
H-Beams: Also known as wide flange beams, H-beams have a cross-section that resembles the letter “H.” They feature two parallel flanges connected by a web, giving them a wider and thicker profile. The flanges are generally wider than those of I-beams, which allows for greater weight distribution and resistance to bending.
I-Beams: These beams have a cross-section shaped like a letter “I.” They consist of two vertical flanges connected by a thinner web. I-beams are typically lighter and can be easier to handle than H-beams. However, their narrower flanges can lead to different structural behaviors under load.
Strength and Load-Bearing Capacity
When evaluating the strength of H-beams and I-beams, it’s essential to consider their load-bearing capacities. The strength of a beam depends on several factors, including its material, size, shape, and the direction of the load applied.
Bending Strength: H-beams tend to outperform I-beams in bending strength. The wider flanges of H-beams allow for a greater moment of inertia, which is a measure of an object’s resistance to bending. This means that H-beams can better handle heavy loads without significant deformation.
Shear Strength: Both H-beams and I-beams exhibit good shear strength; however, the design of the H-beam gives it an edge in certain applications. The wider flanges can distribute shear forces more effectively, making H-beams preferable in situations where shear loads are a concern.
Compression Strength: In compression scenarios, H beams also show superiority due to their larger cross-sectional area. This allows them to support more weight without buckling compared to I-beams of similar height.
Weight and Material Efficiency
One of the significant advantages of I-beams is their weight efficiency. While they are generally not as strong as H-beams, their lighter profile can be beneficial in applications where reducing overall weight is crucial. This makes I-beams easier to transport and install, especially in smaller projects or areas with weight restrictions.
Moreover, in terms of material usage, I-beams may sometimes provide sufficient strength for specific applications while using less material. This can lead to cost savings and a lower environmental impact, as less steel is required for construction.
Applications and Use Cases
The choice between H-beams and I-beams often depends on the specific requirements of a project.
H-Beams: Due to their superior strength and load-bearing capacity, H-beams are commonly used in heavy construction applications. They are ideal for large buildings, bridges, and industrial structures where substantial loads need to be supported. Their design allows them to handle bending, shear, and compression forces effectively.
I-Beams: These beams are more frequently used in residential construction and lighter commercial applications. They are suitable for floor joists, roof supports, and smaller structural elements. Their lighter weight makes them easier to work with in projects where heavy lifting equipment may not be available.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while both H-beams and I-beams have their strengths and applications, H-beams generally provide greater load-bearing capacity and strength due to their wider flanges and thicker profiles. However, I-beams offer advantages in terms of weight and material efficiency, making them suitable for lighter constructions.
Ultimately, the choice between H-beams and I-beams should be guided by the specific requirements of the project, including load conditions, cost considerations, and ease of handling. Understanding the unique characteristics of each beam type will ensure that the most appropriate and effective solution is chosen for any construction endeavor.
Post time: Sep-25-2024