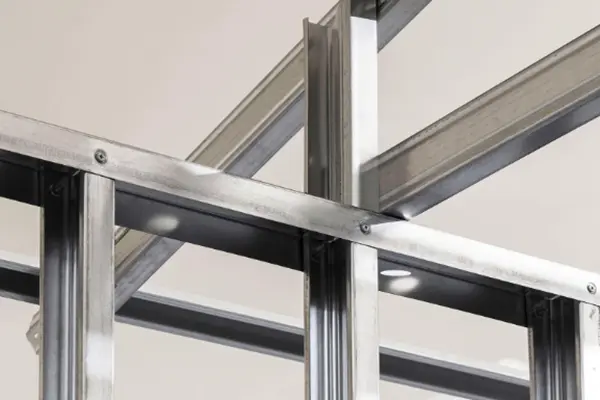
Metal studs, while offering certain advantages such as durability and fire resistance, are not without their drawbacks. Understanding these limitations can help builders and homeowners make informed decisions about their construction projects.
1. Thermal Conductivity:
Metal studs are excellent conductors of heat. This means that they can transfer heat more efficiently than wood studs, leading to potential energy efficiency issues. In colder climates, metal studs can contribute to heat loss, increasing heating costs. Conversely, in warmer climates, they can conduct heat into the interior of a building, making it more difficult to maintain a comfortable temperature. To mitigate this problem, builders often use insulation materials that are specifically designed for metal framing.
2. Noise Transmission:
Metal studs can be more susceptible to noise transmission than wood studs. This is due to their ability to vibrate and transmit sound waves more effectively. As a result, buildings constructed with metal studs may experience higher noise levels between rooms or floors. To address this issue, builders can use soundproofing materials such as acoustic insulation or resilient channels.
3. Corrosion:
Metal studs, especially those made of steel, are susceptible to corrosion. If exposed to moisture or other corrosive elements, metal studs can rust and deteriorate over time. This can lead to structural damage and safety concerns. To prevent corrosion, metal studs should be treated with appropriate protective coatings or finishes. Additionally, they should be installed in a way that minimizes exposure to moisture.
4. Cost:
Metal studs can be more expensive than wood studs, depending on the specific type of metal and the market conditions. This increased cost may be offset by the potential long-term benefits of metal studs, such as durability and fire resistance. However, it is important to consider the overall cost of the project, including the cost of additional materials or labor required for metal framing.
5. Environmental Impact:
The production and transportation of metal studs can have a negative impact on the environment. The extraction of raw materials, manufacturing processes, and transportation can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and other environmental pollutants. While metal studs are often considered more sustainable than wood studs in terms of fire resistance and durability, it is important to evaluate the entire life cycle of the material to assess its environmental impact.
6. Aesthetics:
Metal studs can present challenges for interior finishes. The visible metal framing can create a more industrial or contemporary aesthetic, which may not be desirable in all applications. To conceal metal studs, builders can use drywall or other finishing materials that are designed to cover the framing.
7. Installation Challenges:
Metal studs can be more difficult to install than wood studs, especially for DIY projects. They may require specialized tools and techniques, and they can be heavier and more challenging to handle. Additionally, metal studs may not be as compatible with certain types of fasteners or connectors.
In conclusion, metal studs offer a number of advantages, but they are not without their drawbacks. Understanding these limitations can help builders and homeowners make informed decisions about whether metal studs are the right choice for their construction projects. By carefully considering factors such as thermal conductivity, noise transmission, corrosion, cost, environmental impact, aesthetics, and installation challenges, it is possible to select the most appropriate framing material for a given application.
Post time: Oct-18-2024