When it comes to constructing walls, partitions, and frameworks for buildings, metal studs are a popular alternative to traditional wood framing. These studs offer several advantages, including durability, fire resistance, and ease of installation. However, when selecting metal studs for a particular project, understanding the thickness of the metal is crucial, as it impacts the strength, weight, and overall structural integrity of the framework. One common size of metal stud is the 12 gauge metal stud, but how thick is a 12 gauge metal stud exactly? Let’s explore this in more detail.
Understanding the Gauge System
Before diving into the thickness of a 12 gauge metal stud, it’s important to understand how the gauge system works. The gauge (or “g.”) of a metal refers to its thickness, and it is a measurement used primarily for sheet metal, including steel and aluminum. The lower the gauge number, the thicker the material is. Conversely, a higher gauge number indicates a thinner sheet of metal.
For example:
-
14 gauge metal is thicker than 16 gauge metal.
-
10 gauge metal is thicker than 12 gauge metal.
In the United States, the most commonly used standard for metal gauge thickness is based on the American Wire Gauge (AWG) system, which applies to a variety of metals, including steel.
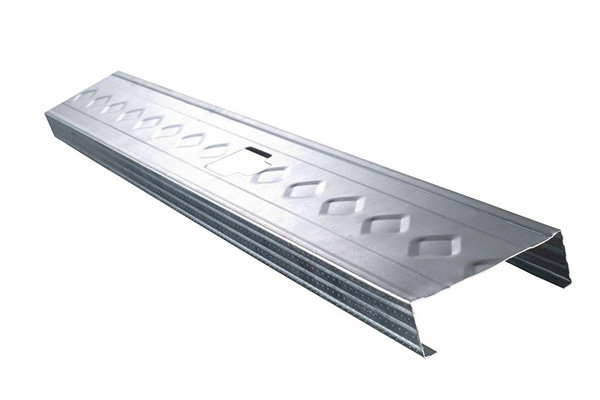

Thickness of a 12 Gauge Metal Stud
Now that we know the basics of the gauge system, let’s get into the specifics of a 12 gauge metal stud. For steel studs, 12 gauge typically corresponds to a thickness of 0.105 inches or 2.67 mm. This measurement can vary slightly depending on the manufacturer, as some may use slightly different processes for rolling or forming the metal, but 0.105 inches is the standard for 12 gauge steel.
To put this in perspective, here’s a comparison of the thickness of different gauge steel:
-
10 gauge: 0.1345 inches (3.42 mm)
-
12 gauge: 0.105 inches (2.67 mm)
-
14 gauge: 0.0781 inches (1.98 mm)
-
16 gauge: 0.0625 inches (1.59 mm)
As you can see, a 12 gauge metal stud is quite thick compared to higher gauges, offering a strong and sturdy material for structural support.
Why Choose 12 Gauge Metal Studs?
The thickness of a metal stud directly affects its strength, load-bearing capacity, and suitability for specific applications. 12 gauge metal studs strike a balance between strength and weight, making them ideal for a variety of construction projects. Here are some reasons why builders might choose 12 gauge studs:
1. Strength and Durability
A 12 gauge metal stud is strong enough to support moderate loads while remaining light enough to be easy to handle during installation. It offers excellent resistance to bending and warping, making it a reliable choice for structural framing, especially in load-bearing walls.
2. Fire Resistance
One of the main advantages of metal studs over wood is their fire resistance. Steel does not burn, so a 12 gauge metal stud can offer an added layer of safety in commercial or residential buildings where fireproofing is a priority.
3. Cost-Effective and Versatile
Although 10 gauge studs are stronger, they are also more expensive and heavier, making them less practical for general construction. On the other hand, 12 gauge studs offer a good compromise between strength and affordability, making them a popular choice for non-load bearing and light-to-medium load applications.
4. Corrosion Resistance
Steel used for metal studs is often galvanized or coated to prevent rust and corrosion. This makes 12 gauge metal studs ideal for use in areas with high humidity, such as bathrooms or basements, where moisture resistance is important.
Applications of 12 Gauge Metal Studs
12 gauge metal studs are commonly used in a variety of construction applications, including:
-
Commercial Construction: 12 gauge studs are often used for framing partition walls in commercial buildings, such as offices, hospitals, and schools.
-
Residential Construction: While 12 gauge studs are more commonly seen in commercial settings, they are sometimes used in residential construction for framing internal walls, especially when additional strength is required.
-
Ceiling Systems: In ceiling grid systems, 12 gauge metal studs can provide the necessary strength to support ceiling panels and other fixtures.
-
Fireproofing: Due to their fire-resistant properties, 12 gauge metal studs are often used in areas where fireproofing is a critical factor.
How Do 12 Gauge Metal Studs Compare to Other Gauge Sizes?
When selecting metal studs for a project, it’s important to consider the specific requirements of the application. The thickness of the stud will influence the overall weight, strength, and load capacity of the framing. Here’s a quick overview of how 12 gauge metal studs compare to other common gauge sizes:
-
10 gauge: Thicker and stronger, often used in heavy-duty applications like large load-bearing walls or exterior frames in harsh environments.
-
14 gauge: Lighter and more flexible, suitable for non-load-bearing walls and partitions in both commercial and residential buildings.
-
16 gauge: The thinnest commonly used stud, typically used for light-duty applications and internal partitions where minimal strength is required.
Choosing the right gauge for your project depends on factors such as the load-bearing requirements, fire resistance, and cost considerations.
Conclusion
A 12 gauge metal stud has a thickness of approximately 0.105 inches (2.67 mm), offering a good balance of strength, durability, and affordability. It is commonly used in both commercial and residential construction for framing, partitioning, and ceiling systems. Understanding the gauge system and knowing the thickness of the materials you’re working with is crucial for ensuring the success of any construction project. Whether you’re building a new home, renovating an office, or constructing a warehouse, 12 gauge metal studs provide a reliable and cost-effective solution for your framing needs.
Post time: Apr-23-2025